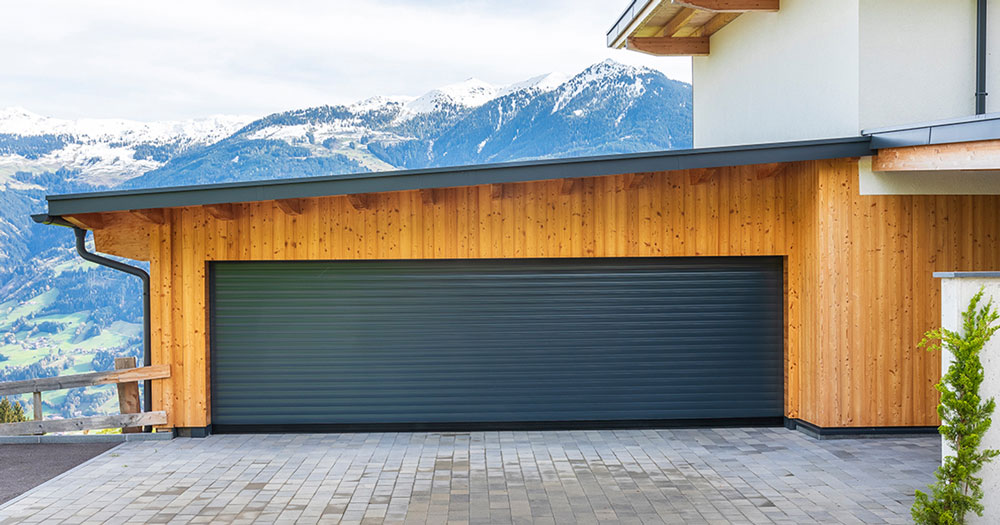
Choosing between repairing or replacing siding can significantly impact your home’s longevity and appearance. The decision hinges on various factors, including the extent of damage, cost, and long-term benefits. We will explore the key considerations to help you determine the most suitable approach for your siding needs. Understanding these factors will guide you in making an informed decision that balances immediate needs with future goals.
Evaluating the Extent of Damage
When deciding between siding repair and replacement, assessing the damage is crucial. Repairs might be sufficient if only a few panels or sections are damaged. Common issues that can be repaired include small cracks, holes, or warping. Minor damage is often fixable with patching and repainting, which can restore the siding’s functionality and appearance without the cost of full replacement. However, replacement might be a more practical solution if the damage is widespread, such as significant rotting, mold, or structural issues affecting multiple panels. Comprehensive damage can compromise the siding’s protective qualities, necessitating a full overhaul to ensure durability and prevent further problems. Evaluating the extent of the damage involves inspecting the siding thoroughly or consulting a leading siding contractor in Portlandfor an assessment to determine whether repairs or replacement is more cost-effective and beneficial.
Cost Considerations
Cost is a significant factor in deciding whether to repair or replace siding. Repairs are typically less expensive than a full replacement, making them an appealing option for homeowners on a tight budget. However, the cost of repairs can add up if the siding is extensively damaged or requires frequent maintenance. Replacing siding involves a higher upfront investment but can offer long-term savings by reducing the need for ongoing repairs and improving energy efficiency. New siding often comes with warranties that cover potential issues, providing additional financial protection. It’s essential to consider the immediate costs of repairs and the possible long-term expenses associated with maintaining or replacing the siding. A detailed cost analysis, including estimates for repair and replacement, will help you make a decision that aligns with your budget and financial goals.
Long-Term Benefits
Weighing the long-term benefits of repair versus replacement is vital in making a well-rounded decision. Repairing siding can extend its lifespan and restore its appearance, but it may not address underlying issues or improve overall performance. On the other hand, replacing siding can enhance your home’s insulation, energy efficiency, and curb appeal. New siding options often come with advanced materials and technology that offer superior protection against weather conditions and lower maintenance requirements. Replacing siding can also increase your home’s market value, making it a valuable investment if you plan to sell. Consider how long you plan to stay in your home and whether the potential improvements in energy efficiency, aesthetics, and property value are worth the higher replacement cost.
Maintenance and Durability
The maintenance and durability of siding play a significant role in the decision to repair or replace. Older siding materials may require frequent upkeep, such as repainting or sealing, to maintain their appearance and functionality. Repairing damaged sections of older siding might only provide a temporary fix, with ongoing maintenance needs becoming a recurring concern. Newer siding materials often offer improved durability and lower maintenance requirements, reducing the need for frequent repairs and maintenance. Relying on aging siding with modern options can provide long-term benefits, including better resistance to weather, pests, and other environmental factors. Evaluating your current siding’s condition and maintenance needs will help you determine whether investing in repairs or replacement will be more practical and cost-effective in the long run.
Aesthetic and Home Value Considerations.
Aesthetic appeal and home value are essential when deciding between repair and replacement. If your current siding is outdated or mismatched with your home’s style, repairs might not fully address aesthetic concerns. Replacing siding offers an opportunity to update your home’s appearance, choose new materials, and enhance its overall look. New siding can also boost your home’s market value, which can be particularly advantageous if you plan to sell. Prospective buyers often appreciate well-maintained and visually appealing siding, which can influence their perception of the property’s value. Assess how necessary the aesthetic improvements and potential increase in home value are to you when deciding between repair and replacement.
Energy Efficiency and Insulation.
Energy efficiency and insulation are significant factors in siding decisions. Older siding materials may need adequate insulation, leading to increased energy costs and reduced comfort inside the home. Repairing damaged siding might not improve its insulation properties or address energy inefficiencies. Replacing siding with modern, energy-efficient materials can enhance your home’s insulation, potentially reducing heating and cooling costs. New siding options often include advanced insulation features that improve thermal performance and energy efficiency. If energy savings and enhanced comfort are priorities, replacing your siding could offer substantial long-term benefits compared to repairing existing materials.
Deciding between siding repair and replacement involves evaluating the extent of damage, cost implications, long-term benefits, maintenance needs, aesthetic considerations, and energy efficiency. Repairs might be suitable for minor damage and immediate budget constraints, but replacement can offer significant advantages in durability, energy efficiency, and home value. Choosing the right approach will ensure your siding effectively protects and enhances your home for years.