Cranioplasty is the reconstruction of a part of the skull cap: an analysis of the procedure, the materials used and the post-procedure aesthetic and functional impact.
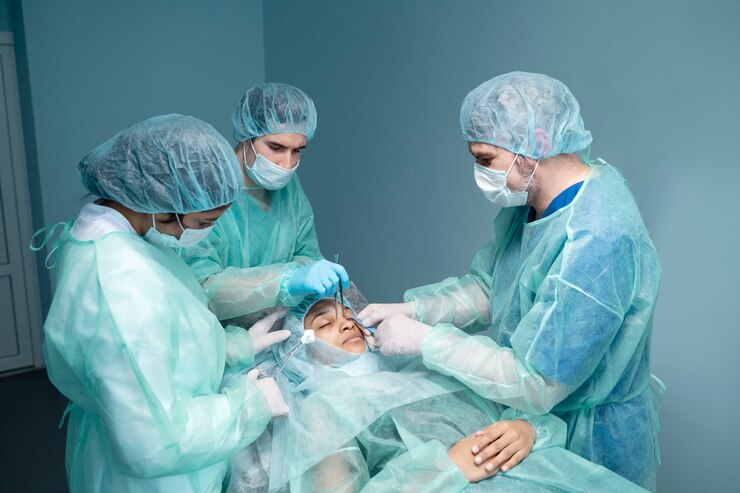
Cranioplasty is part of reconstructive neurosurgery, and involves rebuilding a more or less extensive part of the skull cap.
It is an operation that requires great care, particularly in the pre-operative planning and reconstruction phase, to create a prosthesis capable of adapting and integrating harmoniously with the surrounding bone.
Today’s technology makes it possible to reconstruct even large and complex calvarial solutions, using biocompatible materials that deliver optimal aesthetic and functional results.
Why rebuild the skull?
Cerebral protection: The skull protects the brain from impact. Reconstruction is essential to ensure this vital function.
Symptom reduction: The absence of a part of the skull can lead to headaches, dizziness, difficulty concentrating, balance problems, loss of sense of smell or taste, and even psychological disorders.
Improved aesthetics: Cranial deformity can have a significant impact on the patient’s physical appearance and psychological well-being.
Prevention of complications: Reconstruction prevents the brain from sinking in the event of further trauma, reduces the risk of infection and improves healing.
Cranioplasty surgery is performed in cases where :
there is a bone deficit (craniolacunia) ;
a skull fracture has occurred;
cranial decompression surgery has been performed;
it is necessary to reconstruct the cranial apparatus following bone removal due to tumor invasion.
The conditions listed above can be caused by a variety of factors, such as:
degenerative pathologies ;
congenital skull malformations;
severe head trauma ;
bone resorption;
infections following repositioning of autologous bone;
Trepanning syndrome ;
cerebral hemorrhage or ischemia (leading to increased intracranial pressure).
In the event of increased intracranial pressure, a cranioplasty is performed after a craniectomy, an emergency treatment in which part of the skull is removed.
Cranioplasty surgery in Turkey
Cranioplasty surgery in Turkey mainly involves CT analysis to define the morphological characteristics of the prosthesis.
Both autologous tissue (directly from the patient) and biocompatible prostheses can be used for reconstruction.
The prosthesis has to be designed with many aspects in mind, so it is first designed on the basis of CT scan information.
Based on the CT scan, complex software is able to reconstruct three-dimensional prostheses that are absolutely perfect for the defect to be repaired.
Underestimating this step can lead to evaluation errors, which could make the final result unsatisfactory for the patient (flat head), even if it is functionally acceptable.
To achieve the best results, we use the most modern technologies, as they offer possibilities that were unimaginable in the past, defining new ways of performing surgery.
Turquie santé is your ideal partner for cranioplasty surgery in Turkey. We offer a selection of attractive packages for quality medical treatment in Turkey, while guaranteeing competitive prices. Thanks to our network of reputable clinics, you’ll have access to experienced professionals and modern facilities, so you can concentrate on your recovery with complete peace of mind. Please contact us for more information and to find out how we can help you on your healthcare journey.
Materials
In the latter case, porous hydroxyapatite is used, a material capable of mimicking cranial tissue, so as to integrate perfectly with the surrounding bone (osseointegration): this process is completed a few months after the operation.
Other materials used include synthetic bioplastics such as PEEK .
Risks of cranioplasty
Modern cranioplasty has a low complication rate compared to previous techniques; it is not, however, free of them.
These may include :
Accumulation of fluid in the cerebral ventricles (hydrocephalus);
Infection of the prosthesis or autologous tissue
CSF fistula ;
development of cognitive deficits;
vegetative state.
It’s important to emphasize this aspect, as this is a safe surgical treatment, but complications can also be serious, so evaluation must be thoughtful and conscious.
The different cranioplasty techniques
The choice of technique depends on several factors, such as the extent of the lesion, the nature of the bone to be replaced, and the patient’s general state of health.
Autograft: The bone used for reconstruction comes from another part of the patient’s body, often from the iliac crest. This technique offers excellent integration of the implant, but can be a source of additional pain for the patient.
Customized prostheses: Made from biocompatible materials (titanium, polyethylene), these prostheses are custom-designed to fit the patient’s skull perfectly. They offer good resistance and aesthetic integration, but can be expensive.
Hydroxylapatite: This synthetic material resembles natural bone and can be used alone or in combination with other materials. It offers good biocompatibility and strength.
Cranioplasty is a complex surgical procedure requiring recognized expertise. It offers numerous benefits to patients, improving their quality of life and well-being. Technological advances now make it possible to offer ever more personalized and effective solutions.